Welcome! My name is 方(Fang) 啸(Xiao). Call me Mike if you like.
I worked as a Cloud Engineer at Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and participated in the Cloud-Native migration of Primavera Cloud. Before that, I worked as a Full-Stack Engineer at Moberg Analytics and contributed to the early design and development of CONNECT (the predecessor of Moberg AI Ecosystem).
Currently, I am pursuing my master’s degree at the CSE department of UC San Diego. My research interests hold in multiple areas associated with LLMs, from Knowledge Graphs, Adversarial Attack, PEFT (LoRA, P-Tuning), to ML System (Efficient Inference Architecture). I have 2 publications in top AI conferences, with 20 citations. Feel free to reach out via email if you are interested in collaboration!
I completed my undergraduate at Drexel University and was awarded as the Outstanding Research Assistant of 2023 under the guidance of Professor Yuan An.
🔥 Updates
- 2024.09: 🎉 Joined UC San Diego! La Jolla is awesome 🐳
- 2024.06: 🎉 Graduate from Drexel. Bye Philly 👋
- 2023.12: 🎉 Awarded as the annual Outstanding Research Assistant at Drexel CCI ✨
💻 Experiences
- 2023.10 - 2024.04, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Cloud Software Engineer, Philadelphia.
- 2023.09 - 2024.06, Drexel University, Teaching Assistant, Philadelphia.
- INFO101 - Intro to Computing Technology
- INFO210 - Database Management Systems
- INFO323 - Cloud Computing and Big Data
- 2022.09 - 2023.04, Moberg Analytics, Full-Stack Engineer, Philadelphia.
- Speaker, Multimodal Report Mining Proposal, 2022.11 (slides)
- Speaker, Chrome Debugger Tools & Experience Workshop, 2023.04
- 2022.08 - 2023.05, Drexel University - CCI, Research Assistant, guided by Professor Yuan An, Philadelphia.
- 2020.06 - 2020.09, HFUT - Network Security Center, Network Operation Assistant, Hefei.
📖 Educations
- 2024.00 - 2025.12 (anticipate), UC San Diego, Master of Computer Science.
- 2021.09 - 2024.06, Drexel University, Bachelor of Data Science & Computer Science.
- Member, Data Science Research Club
- A. J. Drexel Scholarship, 2021 / 2022 / 2023
- 2019.09 - 2023.06, Lanzhou University, Bachelor of Computer Science & Engineering.
- Honors Student Scholarship, 2019 / 2020
🎖 Honors
- Outstanding Research Assistant Award, Drexel University, College of Computing and Informatics, 2023
- Knowledge Base Construction Challenge using Language Model (LM-KBC), Second Prize, 2022
- Provincial Prize, China Mathematical Contest in Modeling, 2020
📝 Publications
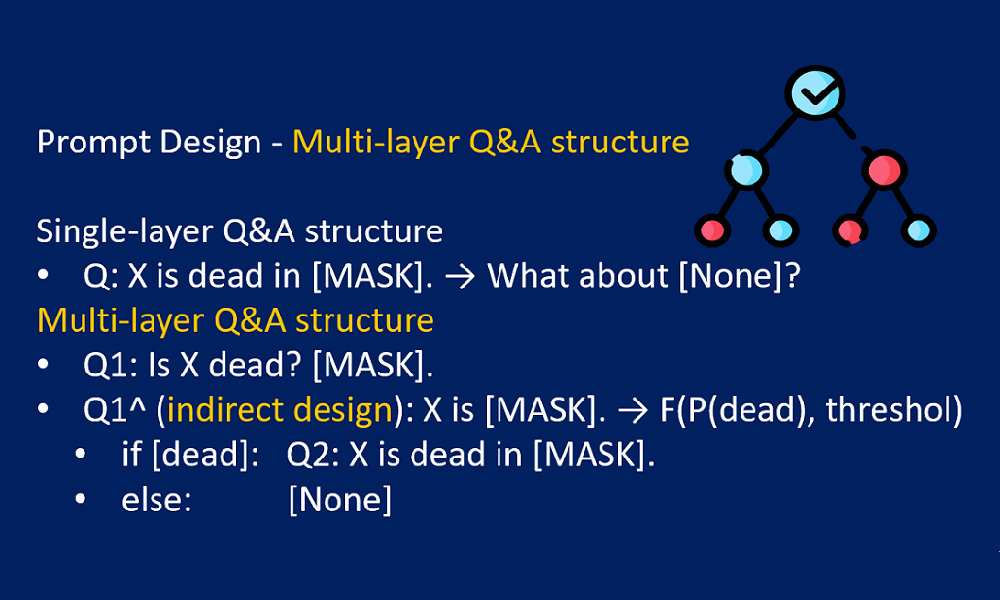
Prompt Design and Answer Processing for Knowledge Base Construction from Pre-trained Language Models (paper)
Xiao Fang, Alex Kalinowski, Haoran Zhao, Ziao You, Yuhao Zhang, Yuan An
The ISWC-2022 challenge on Knowledge Base Construction from Pre-trained Language Models (KBC-LM) provides 12 pre-defined relations. Given a (SubjectEntity, relation) pair, we predicted none, one, or many ObjectEntitys to complete the pair as a triple. The test results on unseen (SubjectEntity, relation) pairs showed our prompt design achieved 49% overall macro average F1-score, a 48% improvement from the baseline’s 31% F1-score. The insights we learned about the “knowledge” of a language model would lead us to select appropriate LMs for future knowledge base construction tasks.
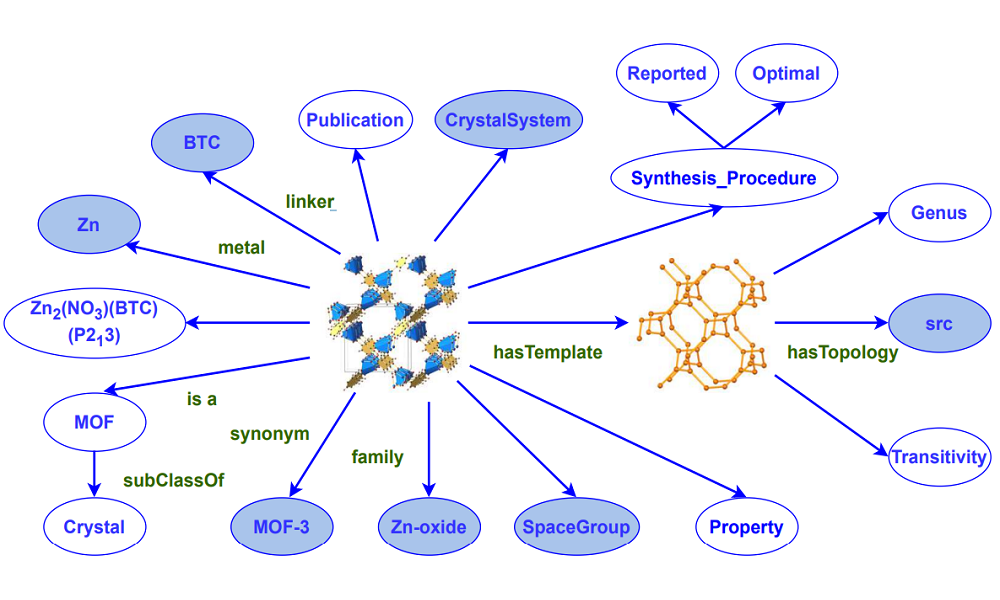
Exploring Pre-Trained Language Models to Build Knowledge Graph for Metal-Organic Frameworks (paper)
Yuan An, Jane Greenberg, Xiaohua Hu, Alex Kalinowski, Xiao Fang, Xintong Zhao, Scott McCLellan, Fernando J Uribe-Romo, Kyle Langlois, Jacob Furst, …
We explored a set of SOTA pre-trained general-purpose and domain-specific language models to extract knowledge triples for metal-organic frameworks. We created a knowledge graph benchmark with 7 relations for 1248 published MOF synonyms. Our experimental results showed that domain-specific PLMs consistently outperformed the general-purpose PLMs for predicting MOF related triples.
💭 Projects - View Full List
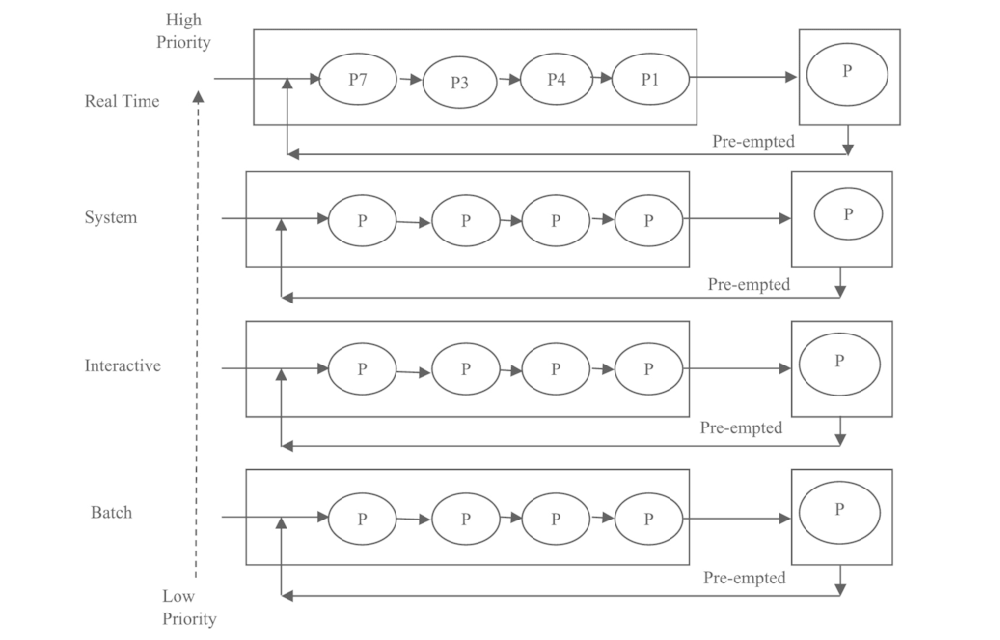
Kernel Component Development Based on UMIX (tester)
-Implemented context switching between processes using Yield, enabling efficient time sharing. Developed a user-level multithreading management system, supporting concurrent execution within a single process.
-Designed and implemented multiple scheduling algorithms, including Round Robin, MLQF, and Stride Scheduling. Addressed MLQF starvation through periodic priority resets. For Stride Scheduling, resolved numerical overflow with Pass Normalization and derived the safe upper bound for L-values by numerical analysis, achieving the optimal precision limit.
-Built a synchronization mechanism based on Semaphores, applying it to a single-lane bidirectional-traffic scheduling model, avoiding busy waiting and ensuring minimal average turnaround time.
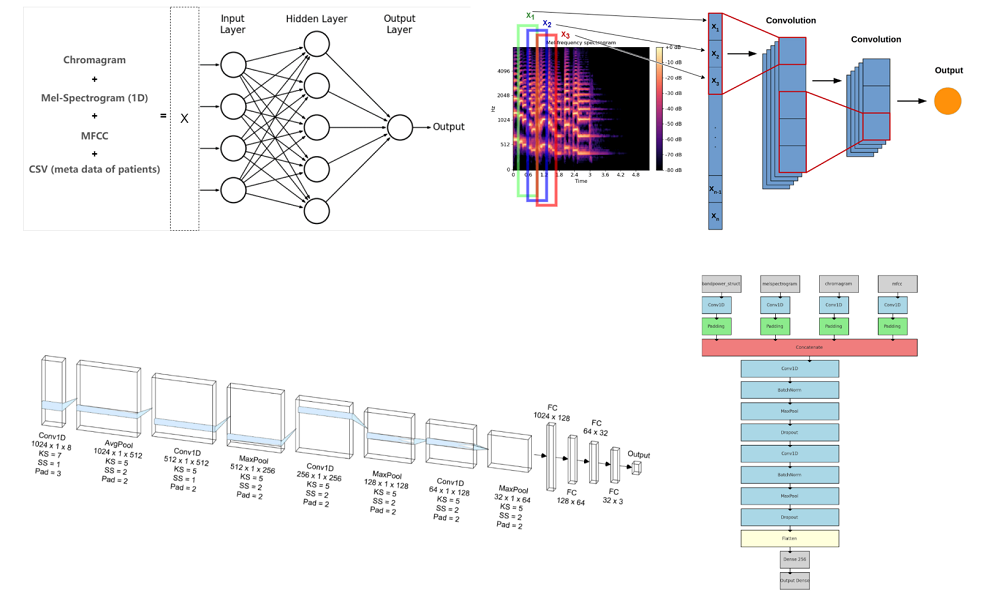
Deep Learning for Heart Disease Prediction (poster|report)
Xiao Fang, Ziao You, Weijie Chen, Yixuan Song, Kan Kim
-Processed a large-scale dataset (33.5 hours of audio), including filtering out non-heartbeat segments, frequency thresholding, and data augmentation through audio subsetting.
-Derived key audio attributes including Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (FMCC), band power, chromagram, and Mel-spectrograms, combining them with patient demographics information to provide a richer feature representation.
-Implemented and tested various ML pipelines: MLPs, CNNs, RNNs, and ensemble models. Achieved the highest accuracy with an Voting-MOE MLP pipeline trained on different feature sets (66%) and a CNN trained on concatenated features (64.22%), significantly outperforming the RNN baseline (50%).
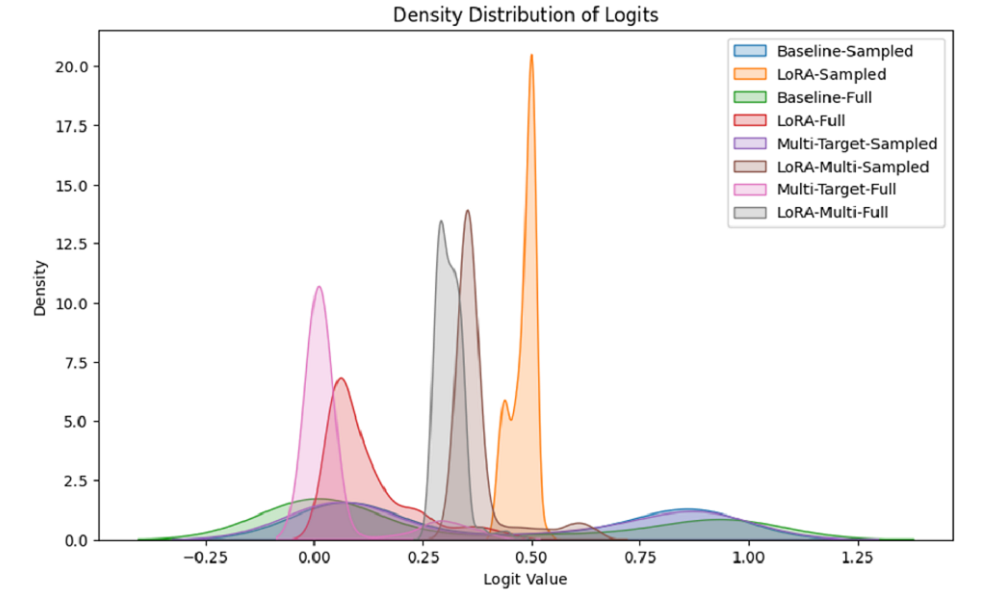
Adapting Toxicity Detection from Comments to Conversational Corpus (report)
-Performed balanced down sampling and conducted fine-tuning experiments on both the imbalanced and sampled datasets for fairness because the lmsys/Toxic-Chat dataset is highly imbalanced, with 92.5% toxic samples.
-Applied Knowledge Distillation (KD) to transfer multi-faceted toxicity evaluation knowledge from the OpenAI Moderation API to the Unitary Toxic BERT model, enhancing model robustness.
-Employed Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning with LoRA, reducing the number of updated parameters to only 0.4% of the full-parameter fine-tuning method, while shortening training time by 12%.
-Optimized multi-objective training through hyperparameter tuning, balancing the primary toxicity detection and KD objectives, leading to a 45% F1-score improvement over the pure-PEFT strategy.
